#x Problem Solving Questions
Here is a non-exhaustive list of problem-solving questions.
- Pre-read:
- Time and Space Complexity
- Big O CheatSheet
- Worst case scenario to be considered when benchmarking
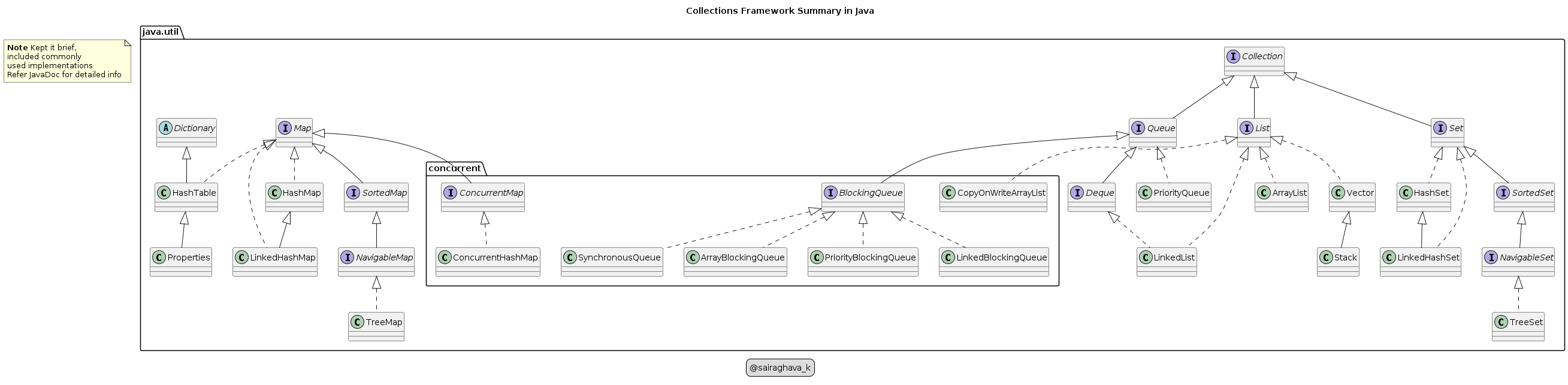
- If Java is your programming language to solve, here is the Collections framework overview chart
Questions
| 1 | fizz-buzz | |
| 2 | Warmup-2 > last2 | Question description is confusing. Focus on sample input and output. Count the last 2 chars substring in given string except the last 2chars |
| 3 | Warmup-2 > arrayCount9 | HINT: Use 2-pointer |
| 4 | Warmup-2 > countXX | |
| 5 | Warmup-2 > stringX | |
| 6 | Warmup-2 > has271 | |
| 7 | Warmup-2 > altPairs | |
| 8 | String1 > minCat | |
| 9 | String-1 > without2 | |
| 10 | String-1 > startWord | |
| 11 | String-1 > withoutX | |
| 12 | String-1 > withoutX2 | |
| 13 | minimum-moves-to-equal-array-elements | |
| 14 | minimum-moves-to-equal-array-elements-ii | |
| 15 | longest-happy-string | |
| 16 | fibonacci-number | |
| 17 | reverse-integer |
NOTE: In math division we have 2 parts - remainder and quotient. In programming we use
%operator to find the remainder and/operator to find the quotient- Example Algorithm/pseudocode
Given a number 123
Divide by 10
123 / 10 = 12(quotient)
123 % 10 = 3(remainder)
initialize 3 vars reverse=0, remainder=0, number=123
while(number != 0) {
remainder = number % 10;
reverse = reverse*10 + remainder;
number /= 10;
}
Finally, the reverse var has the reversed value
| 18 | gcd-of-two-numbers | Refer Algorithm: Euclidian Algorithm |
| 19 | armstrong-number Alternative Link: armstrong-numbers |
|
| 20 | palindrome-number Note: Solve it without converting the input to String |
|
| 21 | Give a string in form of char[] reverse it in place Note: Solve it in-place |
HINT: 2 pointers at front and back, break the loop when i < j and swap chars |
| 22 | two-sum | |
| 23 | three-sum | |
| 24 | contains-duplicate | |
| 25 | valid-anagram | |
| 26 | Valid Parentheses | HINT: java.util.Stack(push, peek, pop) + switch statement |
| 27 | kth-largest-element-in-an-array Note: Solve it without Sorting |
HINT: with offer() load the given array into PriorityQueue(ADT)(Initialize the priority queue as max-heap passing Comparator.reverseOrder()) and poll() the head k times |
| 28 | best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock | |
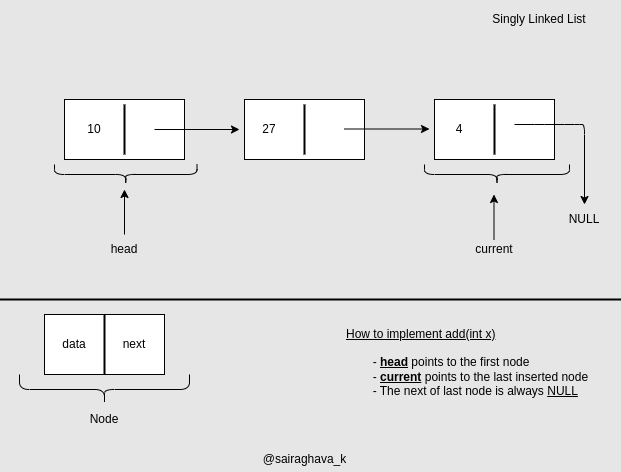
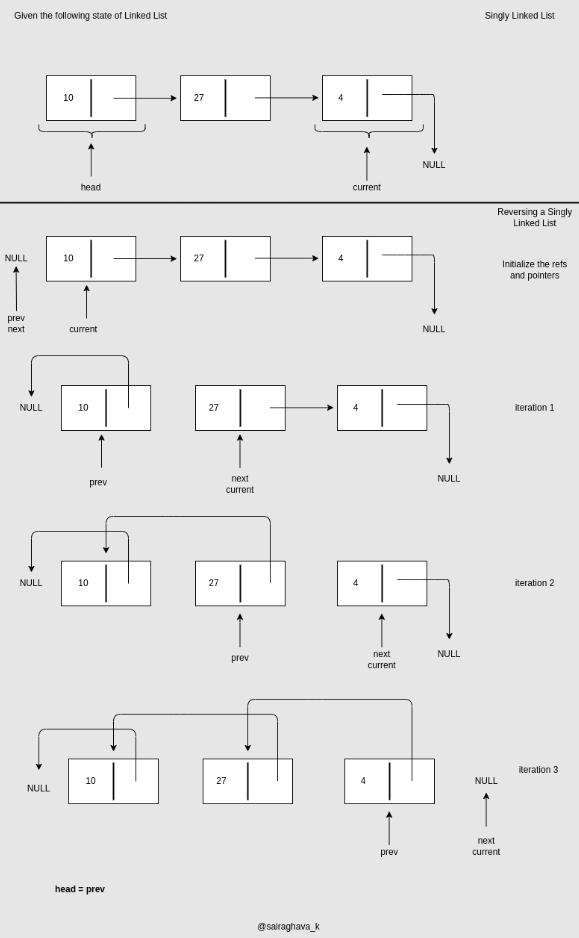
| 29 | Reverse a Linked list |
| 30 | Remove Linked List elements | |
| 31 | Move Zeros | |
| 32 | Max Sub array sum | |
| 33 | Top k Frequent elements | |
| 34 | Rotate array to right k steps | |
| 35 | LRU Cache |
- HINT:
- Option1:
LinkedList(Is a Doubly LinkedList in Java) +HashMap - Option2:
int capacity = 2; LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer> lhs = new LinkedHashMap<>(capacity, 0.75f, true) { @Override protected boolean removeEldestEntry(java.util.Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> eldest) { return size() > capacity; } }; - Option1:
| 36 | Reverse words in a string | |
| 37 | Reverse Words | |
| 38 | Array-1 > unlucky1 |