1-1 JPA Mapping with Spring Boot
This post provides an overview of establishing a 1-1 mapping between 2 entities in JPA. Let’s take an example of Driver, and DriverLicense, wherein each driver will have exactly one driver’s license, and a driver’s license is assigned to a driver.
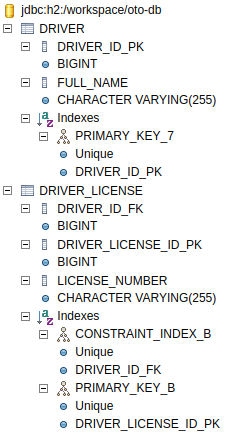
Database Schema:
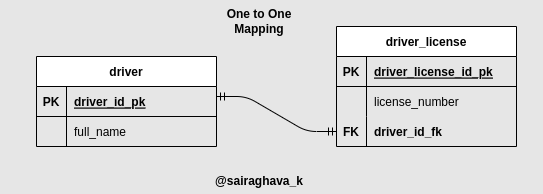
Here is the relationship between the tables driver, and driver_license
JPA Entities:
Spring Boot application with spring-boot-starter-data-jpa dependency comes along with Hibernate as JPA implementation.
Here is the code snippets of entities
-
Driverpackage oto; import jakarta.persistence.Column; import jakarta.persistence.Entity; import jakarta.persistence.GeneratedValue; import jakarta.persistence.GenerationType; import jakarta.persistence.Id; import jakarta.persistence.OneToOne; import jakarta.persistence.Table; import lombok.Getter; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor; @Entity(name = "Driver") @Table(name = "driver") @NoArgsConstructor @Getter public class Driver { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO) @Column(name = "driver_id_pk") private Long id; @Column(name = "full_name") private String fullName; @OneToOne(mappedBy = "driver") private DriverLicense driverLicense; public Driver(String fullName) { this.fullName = fullName; } @Override public String toString() { return "{" + fullName + "}"; } } -
DriverLicensepackage oto; import jakarta.persistence.Column; import jakarta.persistence.Entity; import jakarta.persistence.GeneratedValue; import jakarta.persistence.GenerationType; import jakarta.persistence.Id; import jakarta.persistence.JoinColumn; import jakarta.persistence.OneToOne; import jakarta.persistence.Table; import lombok.Getter; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor; @Entity(name = "DirverLicense") @Table(name = "driver_license") @NoArgsConstructor @Getter public class DriverLicense { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO) @Column(name = "driver_license_id_pk") private Long id; @Column(name = "license_number") private String licenseNumber; @OneToOne @JoinColumn(name = "driver_id_fk", referencedColumnName = "driver_id_pk") private Driver driver; public DriverLicense(String licenseNumber) { this.licenseNumber = licenseNumber; } public void setDriver(Driver driver) { this.driver = driver; } @Override public String toString() { return "{" + licenseNumber + "}"; } }
It is bi-directional mapping because the owning side of the relationship i.e., DriverLicense is able to fetch the associated driver which is obvious, and also the Driver entity is able to fetch the associated DriverLicense.
The key point here is that the owning side of the relationship entity will have the
@OneToOneand@JoinColumnannotation that will establish a uni-directional relationship.And, further to establish the bi-directional relationship we must add
@OneToOne(mappedBy = "fieldName")in other entity i.e.,Driverentity in our example.
Here is the H2 db schema created from the application with configuration spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=create-drop set in application.yaml.
To insert into and retrieve data from these tables we must create a Repository interfaces per each entity say DriverRepository and DriverLicenseRepository and extend them with org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository.
For complete working example of 1-1 JPA mapping demo refer my GitHub repo oto-jpa-mapping-with-spring-boot