1-Many and Many-1 JPA Mapping with Spring Boot
This post focuses on establishing 1-Many and Many-1 relationship between two entities in JPA.
Terminology
- Owning Side or Child Entity: From a database standpoint it’s a table having the foreign key reference of the other tables. And, from JPA standpoint it is an entity having the
@JoinColumnannotation - Non-Owning Side or Inverse Side or Parent Entity: From JPA perspective, it’s an entity having a reference of owning side with
mappedByattribute passed to any of the annotations say@OneToOne,@OneToManyor@ManyToMany
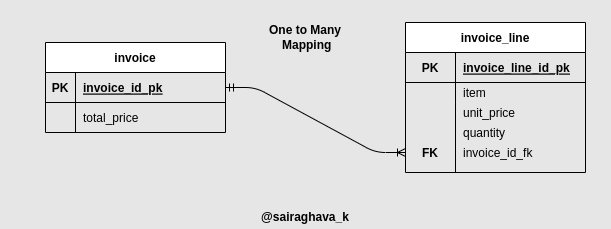
Database Schema:
Here is the relationship between the tables invoice, and invoice_line
JPA Entities:
Spring Boot application with spring-boot-starter-data-jpa dependency comes along with Hibernate as JPA implementation.
Here is the code excerpts of entities
-
Invoicepackage otm.mto; import java.util.Set; import jakarta.persistence.CascadeType; import jakarta.persistence.Column; import jakarta.persistence.Entity; import jakarta.persistence.FetchType; import jakarta.persistence.GeneratedValue; import jakarta.persistence.GenerationType; import jakarta.persistence.Id; import jakarta.persistence.OneToMany; import jakarta.persistence.Table; import lombok.Getter; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor; @Entity(name = "Invoice") @Table(name = "invoice") @NoArgsConstructor @Getter public class Invoice { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO) @Column(name = "invoice_id_pk") private Long id; @Column(name = "total_price") private Double totalPrice; @OneToMany( mappedBy = "invoice", cascade = CascadeType.ALL, // Defaults to no operations being cascaded. orphanRemoval = true, // default is false fetch = FetchType.EAGER) // default is FetchType.LAZY /*- Note: With LAZY fetch it would result in this exception Exception in thread "main" org.hibernate.LazyInitializationException: failed to lazily initialize a collection of role: otm.mto.Invoice.invoiceLines: could not initialize proxy - no Session */ /*- What if the invoiceLines count is huge for a given Invoice * may not applicable for this example * Point is use eager fetching judiciously * Recommended to apply @EntityGraph(attributePaths = {"invoiceLines"}) * on each custom fetch method in InvoiceRespository */ private Set<InvoiceLine> invoiceLines; public Invoice(Double totalPrice) { this.totalPrice = totalPrice; } public void setTotalPrice(Double totalPrice) { this.totalPrice = totalPrice; } public void setInvoiceLines(Set<InvoiceLine> invoiceLines) { this.invoiceLines = invoiceLines; } @Override public String toString() { return "{ invoice_id=" + id + ", totalPrice=" + totalPrice + "}"; } } -
InvoiceLinepackage otm.mto; import java.util.Objects; import jakarta.persistence.Column; import jakarta.persistence.Entity; import jakarta.persistence.GeneratedValue; import jakarta.persistence.GenerationType; import jakarta.persistence.Id; import jakarta.persistence.JoinColumn; import jakarta.persistence.ManyToOne; import jakarta.persistence.Table; import lombok.Getter; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor; @Entity(name = "InvoiceLine") @Table(name = "invoice_line") @NoArgsConstructor @Getter public class InvoiceLine { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO) @Column(name = "invoice_line_id_pk") private Long id; @Column(name = "item") private String item; @Column(name = "unit_price") private Double unitPrice; @Column(name = "quantity") private Integer quantity; public InvoiceLine(String item, Double unitPrice, Integer quantity, Invoice invoice) { this.item = item; this.unitPrice = unitPrice; this.quantity = quantity; this.invoice = invoice; } @ManyToOne @JoinColumn(name = "invoice_id_fk", referencedColumnName = "invoice_id_pk", nullable = false) private Invoice invoice; @Override public String toString() { return "{ item=" + item + ", unitPrice=" + unitPrice + ", quantity=" + quantity + "}"; } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) return true; if (o == null) return false; if (!(o instanceof InvoiceLine)) return false; InvoiceLine that = (InvoiceLine) o; return this.getItem().equals(that.getItem()) && this.getUnitPrice().equals(that.getUnitPrice()) && this.getQuantity().equals(that.getQuantity()); } @Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(item, unitPrice, quantity); } }
This example depicts the Bidirectional association or two-way mapping between Invoice and InvoiceLine entities. In simple English, given an Invoice we can fetch all the associated InvoiceLine and vice versa.
Significance of CascadeType, FetchType, orphanRemoval
jakarta.persistence.FetchTypeFrom the javadoc: Defines strategies for fetching data from the database. The EAGER strategy is a requirement on the persistence provider runtime that data must be eagerly fetched. The LAZY strategy is a hint to the persistence provider runtime that data should be fetched lazily when it is first accessed. The implementation is permitted to eagerly fetch data for which the LAZY strategy hint has been specified.Use of
CascadeType.ALLin Parent EntityInvoice- Child entities will be affected by all these operations on the parent entity. For example, if we delete the parent entity, the associated child entities will also be deleted, similarly if we save/persistInvoicehaving theInvoiceLine, it persists into tableinvoiceobviously and also intoinvoice_linetable.Use of
orphanRemoval = truein Parent EntityInvoice- When we remove a child entity from the parent’s collection, it will be automatically removed (deleted) from the database. For example if we remove anInvoiceLinefrom theInvoiceand save/persist theInvoice, that specificinvoice_linerecord will be deleted frominvoice_linetable
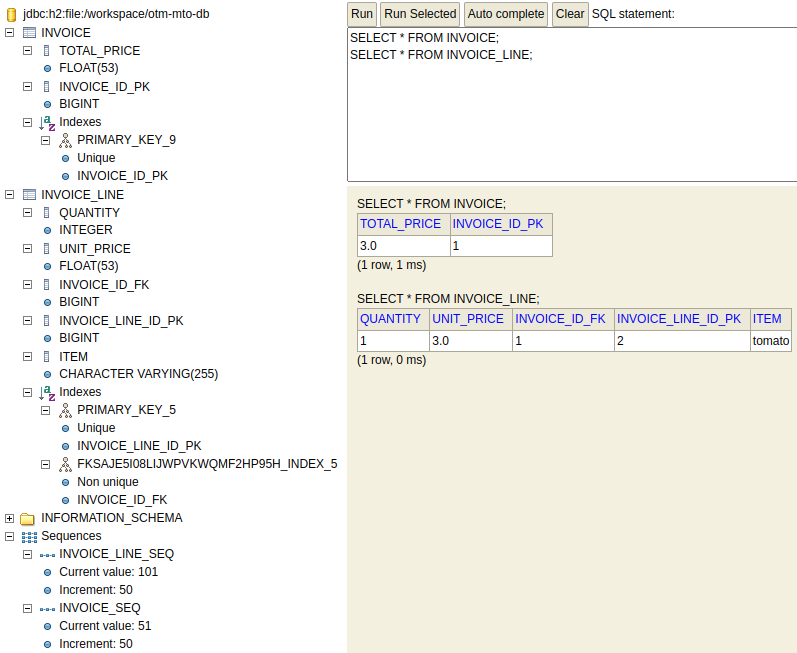
Here is the H2 db schema and its state created from the application having configuration spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=create-drop set in application.yaml.
In sum, we have 2 entities Invoice, InvoiceLine having a dedicated repository interface for each entity like InvoiceRepository and InvoiceLineRepository.
- Having
CascadeType.ALLinInvoiceenables to save/persistInvoiceLinewhenInvoiceis saved to DB. - And, with configuration
orphanRemoval=trueenablesInvoiceentity to deleteInvoiceLinethroughInvoiceRepository.
Refer my GitHub repo otm-and-mto-jpa-mapping-with-spring-boot for complete sample.